Danielle Tan
Chief Operating Officer
Traceability systems have become increasingly important due to rising customer awareness and the complexity of supply networks.

In recent years, food manufacturing companies have increased their focus on transparency and traceability of their products. This has become more important to ensure that the food they produce meets quality standards and is safe for consumption.
Transparency in food manufacturing is the process of being open and honest about the production process. Companies must be clear about their ingredients, processes and sources of food. This means that consumers know exactly what they are buying and that they can trust the food they consume. Transparency also helps to build trust between companies and their customers.
The Standards
| FSSC 22000 version 5.1 ISO 22000:2018 |
8.3 Traceability System |
|---|---|
| Codex HACCP 2020 | 8.1 Lot Identification and Traceability |
| MS 1480:2019 | 7.3 Traceability |
| MS 1514:2022 | 9.3 Traceability |
| BRCGS Food Safety Issue 9 | 3.9 Traceability |
Traceability Requirements based on ISO 22000:2018
The traceability system shall be able to uniquely identify incoming material from the suppliers and the first stage of the distribution route of the end product. When establishing and implementing the traceability system, the following shall be considered as a minimum:
- relation of lots of received materials, ingredients and intermediate products to the end products;
- reworking of materials/ products;
- distribution of the end product.
The organization shall ensure that applicable statutory, regulatory and customer requirements are identified.
Documented information as evidence of the traceability system shall be retained for a defined period to include, as a minimum, the shelf life of the product. The organization shall verify and test the effectiveness of the traceability system.
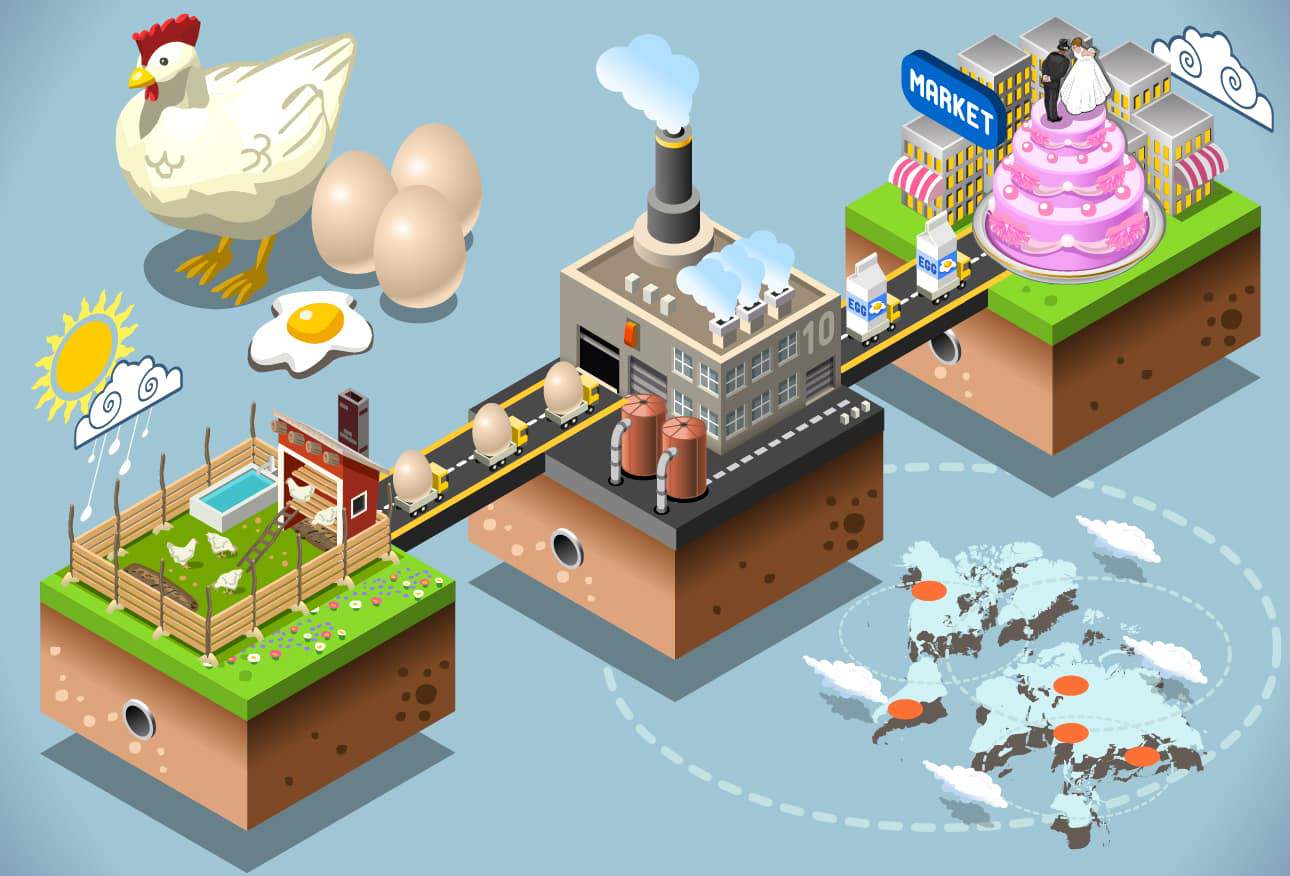

What is Food Traceability?
Food traceability is the ability to follow a food’s production chain, from its raw materials and additives to how it was made and where it was sold. It is a way to make food and drink factories more accountable and open to the public. It is also a way to check on the quality and safety of food at every stage of production.
In order to find out where food and food ingredients came from, the chain of events from production to processing to distribution must be recorded and linked.
Effective product tracing makes it easy for the government, food producers, and food distributors to find out where a product came from and where it might have been contaminated in case of a food-borne illness outbreak or poisoning. This lets the problem product be taken off the market faster, which makes it less likely that someone will get sick from eating it.
5 Key Steps in Developing a Food Traceability System

#1 Identify Key Stakeholders
The first step in developing a food traceability system is to identify the key players and stakeholders in the process. This includes both internal and external parties, such as suppliers, distributors, retailers, customers and relevant government authorities.

#2 Determine the Scope of Traceability System
Once the stakeholders have been identified, the next step is to determine the scope of the system. This includes understanding what type of food products will be tracked and which stages of the supply chain will be included. Companies must also decide on how information will be collected and stored in the system.
Bottom line is the food and ingredients you purchase from vendors and distribute to your business clients must be traceable (excluding food supplied to final consumer). It is important to ensure that the traceability scope meets relevant legal requirements of the country of intended sale.

#3 Establish Tracking Method
The next step is to decide which technology or method will be used to track and store data. This might include an electronic system, such as a barcode scanner, or a more manual system, like paper records. Companies must also decide the type of data that will be stored and how it will be tracked. This can help guarantee reliable food tracking and limit the amount of food that must be withheld or recalled.
The increased focus on transparency and traceability has led to the adoption of several new technologies. These include blockchain, which allows for secure and transparent transfer of data, and RFID (radio frequency identification) tags, which allow companies to track products throughout the supply chain. These technologies have made it easier for companies to meet transparency and traceability requirements.

#4 Record Keeping
Once the system is in place, companies must develop protocols for collecting and storing data. This should include procedures for collecting data at each stage of the supply chain and for ensuring accuracy and consistency of data. Companies should also develop protocols for updating and maintaining the system.
Your traceability records need to be easily accessible when needed.
At a minimum, traceability information to be kept include:
- Address and name of the company.
- Periods of transaction.
- Quantities of product sold.
- Receiving, storage and production data.
- QC inspection and testing records.
- Delivery/ distribution information.
#5 Traceability Test
Test the traceability system and ensure that it is working correctly. Traceability test shall be carried out at planned intervals (e.g. annually) to review the traceability data and making sure that all stakeholders are following the traceability plan. It is also important to make sure that any changes or improvements are made quickly and efficiently.
Bottom Line
Tracking food as it moves through the supply chain allows for more precise food withdrawal and recall procedures in the event that they become necessary. Your ability to quickly and accurately identify the tainted goods, lessen risks to consumers, and cut costs will improve in proportion to the amount of relevant data you collect and store.
Reference/Source:
- https://www.foodbeverageinsider.com/operations/6-vital-food-safety-predictions-2023
- https://www.deskera.com/blog/food-traceability/
- ISO 22000:2018 Food safety management systems – Requirements for any organization in the food chain






