Danielle Tan
Managing Consultant
On September 25, 2020, the Codex Alimentarius Commission adopted the revised Code of Practice (General Principles of Food Hygiene (CXC 1-1969) and its HACCP annex). In this post, find out about some of the changes that may impact your food business.
– 5 mins read

On September 25, 2020, the Codex Alimentarius Commission adopted the revised Code of Practice (General Principles of Food Hygiene (CXC 1-1969).
Compared to the 2003 code revision, there have been numerous changes in Codex HACCP 2020. The standard was updated in 2020, with modifications ranging from minor structure changes to definitions and even the inclusion of new concepts.
What Has Changed from The Previous Codex HACCP Version?

1. Changes in Standard Structure
The standard has been restructured into two parts: Good Hygiene Practices and HACCP Principles. A general principle has been added to the structure of Good Hygiene Practices.
The revised document now has the following structure:
- Introduction
- Objectives
- Scope
- Use General
- Roles of competent authorities, food business operators and consumers
- General principles
- Management commitment to food safety
- Definitions
- Chapter 1 Good Hygiene Practices
- Chapter 2 Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System and Guidelines for Its Application
- Annex 1 Comparison of Control Measures with Examples
- Diagram 1 Logic Sequence for Application of HACCP
- Diagram 1 Example of Hazard Analysis Worksheet
Download the latest version of Codex HACCP 2020 here:
General Principles of Foods Hygiene CXC 1-1969

2. Food Safety Culture
The commitment of leaders in building and sustaining a Food Safety Culture in the organization has been added to HACCP Codex 2020 to ensure the success of the food safety management system.
– Responsibilities and authorities must be communicated inside the organization
– Communication
– Resource supply
– Training to staff
– Legal requirements compliance
– Continuously improvement
Read the article about Food Safety Culture here :

3. Good Hygiene Practices
New and enhanced requirements have been added for:
- Primary production.
- Establishment.
- Establishment maintenance.
- Personal hygiene.

4. Control of Allergens
In addition to physical, chemical, and biological hazards, Codex HACCP 2020 adds to the risk by requiring allergy control. The “Code of Practice on Food Allergen Management for Food Business Operators” outlines the requirements for allergen management (CXC 334-2020).
- Identification of allergens in raw materials.
- Cross-contamination control (storage, cleaning, swab test, …)
- Allergen awareness training.
- Labeling and provide allergen information to customers and consumers.

5. Training and Competence
The training and competency section has been improved. There have been several additional factors that must be considered when evaluating the amount of training required. The following should be included in your training:
- The use and maintenance of instruments and equipment associated with food
- The principles of food hygiene
- Control measures to prevent contaminants in food
- Good hygiene practices
- Corrective actions
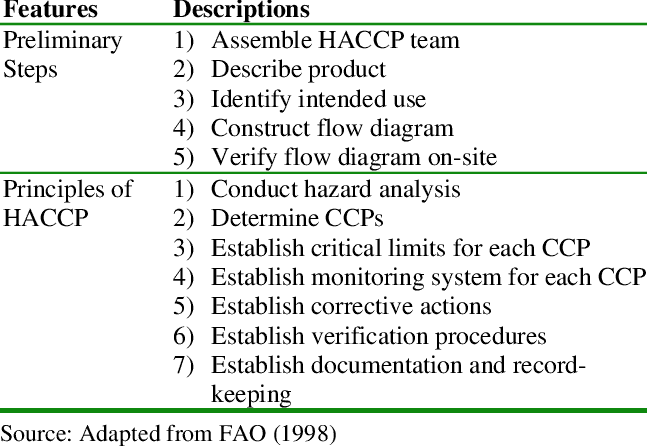
6. Preparation Steps and 7 HACCP Principles
The 12 steps of preparation for HACCP have been added with more details :
Step 1: Assemble HACCP Team and Identify Scope.
Step 2: Describe Product.
Step 3: Identify Intended Use and Users.
Step 4: Construct Flow Diagram.
Step 5: On-site Confirmation of Flow Diagram.
Step 6: Hazard Analysis (Principle 1).
Step 7: Determine the Critical Control Points (CCP) (Principle 2).
Step 8: Establish Validated Critical Limits for Each CCP (Principle 3).
Step 9: Establish a Monitoring System for Each CCP (Principle 4).
Step 10: Establish Corrective Actions (Principle 5).
Step 11: Validation of the HACCP Plan and Verification Procedures (Principle 6).
Step 12: Establish Documentation and Record Keeping (Principle 7).
When defining CCP, the decision tree diagram is no longer the only choice; other technique can be used.

This Codex HACCP code of practice, according to an update on the FAO website, “provides a common ground for the control of food safety globally and serves as the foundation for all other Codex hygiene texts and standards.” The revision includes updates that will help food company owners, regulatory agencies, and other stakeholders apply the standards more effectively.
In addition, the code adds to the adoption of a new Codex code of practices on allergen management by providing greater guidance on the critical health issue of allergens. At a time when the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need to strengthen appropriate hygiene procedures, this revision aids countries in maintaining a continuous safe supply of food.
The general principles section has been included to help describe the standards for controlling food safety concerns. Control measures must be scientifically validated. The food safety control system must be evaluated, reviewed, and corrective actions made as needed on a regular basis. Communication must be in place to ensure that stakeholders and interested parties are kept informed throughout the food supply chain.
What Do I Do Now?
If you are:
- In the midst of applying Codex HACCP, you can apply Codex HACCP 2020 version.
- Certified to Codex HACCP version 2003, you can update it to the new version at the surveillance audit or re-certification audit.
Book a complimentary 30 minutes consultation session with us here or contact us for more information about Codex HACCP 2020.
Reference :
- https://www.bureauveritas.vn/en/newsroom/haccp-codex-new-version-2020
- http://www.correctfoodsystems.com.au/codex-haccp-2020.htm
More Article
Empowering Employees through ESG: The Role of Training and Awareness
Chief Operating OfficerEmpower your team with ESG training. ISO-aligned, practical, and impactful for SMEs in Malaysia.As businesses around the world embrace Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles, a common mistake is treating ESG solely as a boardroom...
ESG for SMEs: Simple Steps to Get Started (Even with a Small Team)
Chief Operating OfficerSimple ESG tips for SMEs. Begin your journey with support from trusted ESG consultants in Malaysia.In today’s business environment, Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) practices are no longer just for large corporations. Small and...
What Is Food Safety Culture and Why It Matters More Than Ever
Chief Operating OfficerLearn why food safety culture is a must-have for compliance, brand trust, and growth—backed by ISO consultants in Malaysia.In today’s competitive and tightly regulated food manufacturing landscape, compliance alone is no longer enough. To...
Why Proactive OSH Legal Compliance Is Good for Business Reputation
Chief Operating OfficerWorried about Malaysia’s OSH Act penalties or workplace audit readiness? Discover how proactive OSH compliance builds trust, reduces fines, and supports ESG goals.In today’s competitive market, companies are judged not just by their products or...










